Years 7 and 8
Learning in Digital Technologies focuses on further developing understanding and skills in computational thinking such as decomposing problems and prototyping; and engaging students with a wider range of information systems as they broaden their experiences and involvement in national, regional and global activities.
By the end of Year 8, students will have had opportunities to create a range of digital solutions, such as interactive web applications or programmable multimedia assets or simulations of relationships between objects in the real world.
In Year 7 and 8, students analyse the properties of networked systems and their suitability and use for the transmission of data types. They acquire, analyse, validate and evaluate various types of data, and appreciate the complexities of storing and transmitting that data in digital systems. Students use structured data to model objects and events that shape the communities they actively engage with. They further develop their understanding of the vital role that data plays in their lives, and how the data and related systems define and are limited by technical, environmental, economic and social constraints.
They further develop abstractions by identifying common elements while decomposing apparently different problems and systems to define requirements, and recognise that abstractions hide irrelevant details for particular purposes. When defining problems, students identify the key elements of the problems and the factors and constraints at play. They design increasingly complex algorithms that allow data to be manipulated automatically, and explore different ways of showing the relationship between data elements to help computation, such as using pivot tables, graphs and clearly defined mark-up or rules. They progress from designing the user interface to considering user experience factors such as user expertise, accessibility and usability requirements.
They broaden their programming experiences to include general-purpose programming languages, and incorporate subprograms into their solutions. They predict and evaluate their developed and existing solutions, considering time, tasks, data and the safe and sustainable use of information systems, and anticipate any risks associated with the use or adoption of such systems.
Students plan and manage individual and team projects with some autonomy. They consider ways of managing the exchange of ideas, tasks and files, and techniques for monitoring progress and feedback. When communicating and collaborating online, students develop an understanding of different social contexts, for example acknowledging cultural practices and meeting legal obligations.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
Achievement Standard
By the end of Year 8, students explain how social, ethical, technical and sustainability considerations influence the design of innovative and enterprising solutions to meet a range of present and future needs. They explain how the features of technologies influence design and production decisions. Students make choices between different types of networks for defined purposes.
Students explain a range of needs, opportunities or problems and define them in terms of functional requirements and constraints. They collect, authenticate and interpret data from a range of sources to assist in making informed judgements. Students generate and document in digital and non-digital form, design ideas for different audiences using appropriate technical terms, and graphical representation techniques including algorithms. They independently and safely plan, design, test, modify and create a range of digital solutions that meet intended purposes including user interfaces and the use of a programming language. They plan, document and effectively manage processes and resources to produce designed solutions for each of the prescribed technologies contexts. They develop criteria for success, including innovation and sustainability considerations, and use these to judge the suitability of their ideas, solutions and processes. Students use appropriate protocols when collaborating, and creating and communicating ideas, information and solutions face-to-face and online.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
Achievement Standard
By the end of Year 8, students distinguish between different types of networks and defined purposes. They explain how text, image and audio data can be represented, secured and presented in digital systems.
Students plan and manage digital projects to create interactive information. They define and decompose problems in terms of functional requirements and constraints. Students design user experiences and algorithms incorporating branching and iterations, and test, modify and implement digital solutions. They evaluate information systems and their solutions in terms of meeting needs, innovation and sustainability. They analyse and evaluate data from a range of sources to model and create solutions. They use appropriate protocols when communicating and collaborating online.
(source: www.australiancurriculum.edu.au)
- Free Plan
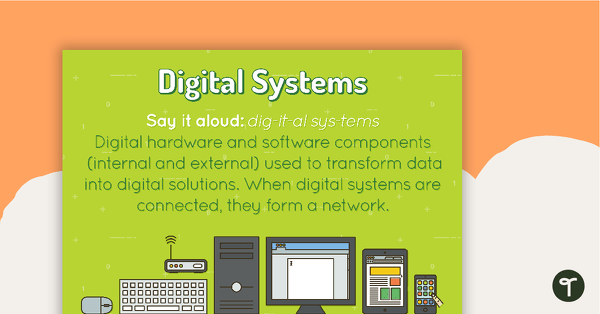
Digital Systems Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of a digital system.
- Free Plan

Binary Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of binary.
- Plus Plan
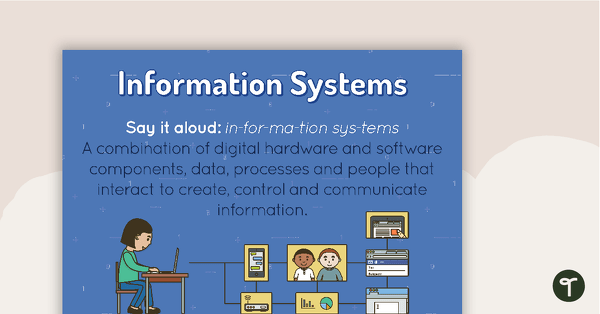
Information Systems Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of Information Systems.
- Plus Plan
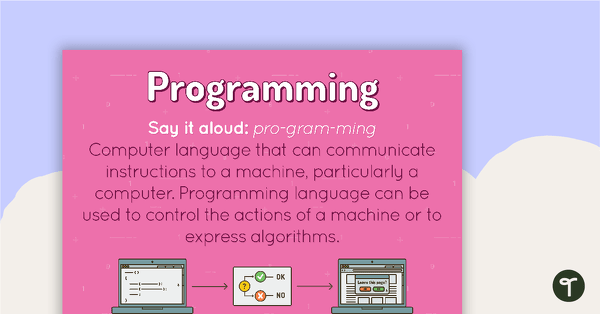
Programming Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of programming.
- Plus Plan
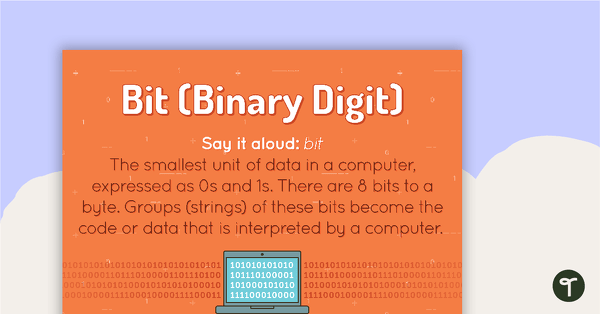
Bit Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of a bit.
- Plus Plan
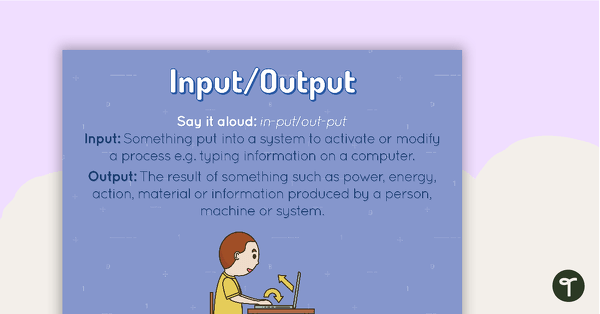
Input/Output Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of an input and an output.
- Plus Plan
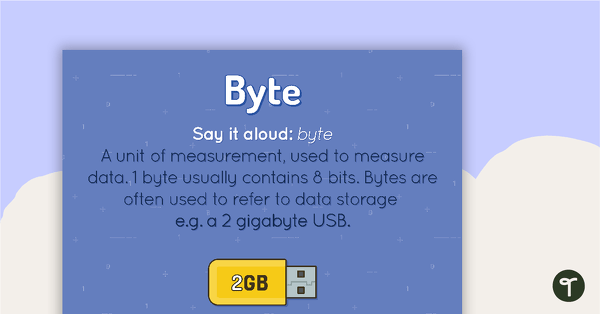
Byte Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of a byte.
- Plus Plan
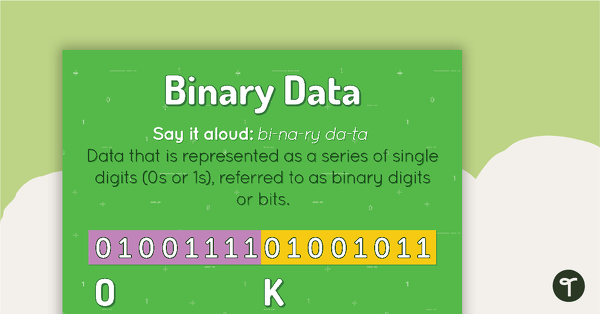
Binary Data Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of binary data.
- Plus Plan

Binary Codes Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of binary codes.
- Plus Plan

Materials Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of materials.
- Plus Plan
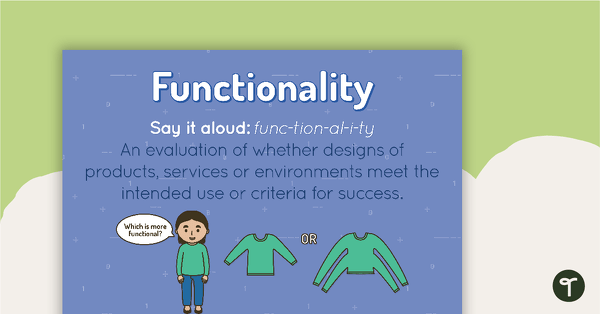
Functionality Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of Functionality.
- Plus Plan
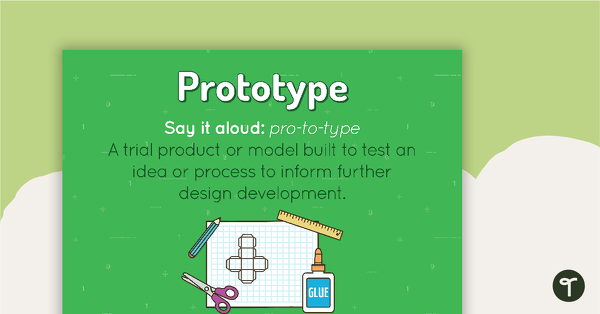
Prototype Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of a prototype.
- Plus Plan
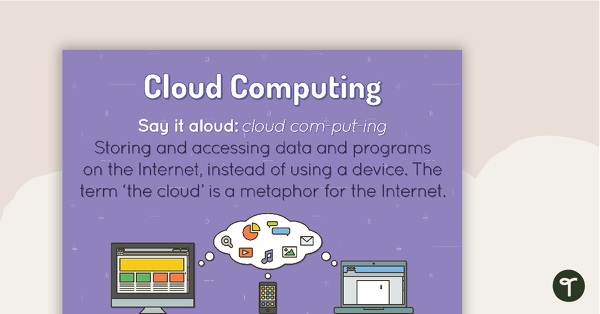
Cloud Computing Poster
A poster showing the definition and an example of cloud computing.