3D Shapes Teaching Resources
Teach 3D shapes with ease using printable worksheets, digital teaching tools, hands-on games and much more from Teach Starter’s extensive collection of three-dimensional shape resources!
This collection of curriculum-aligned teaching resources has been created by Teach Starter’s expert team of teachers to make planning easier for teachers just like you! Familiarize students with 3D shapes and their properties using an extensive range of practical, hands-on and easy-to-implement teaching and learning materials.
Designed to cater to a range of ability levels, our differentiated and editable activities are bound to excite your students as they engage with the important mathematical topic.
Need a refresher on 3D shapes before delving into this concept with your students? Read on for a guide to all things three-dimensional from our experienced teacher team, including a kid-friendly way to explain these shapes and some common examples.
What Are 3D Shapes? A Kid-Friendly Definition
Looking for a simple way to describe 3D shapes to your students? Here's a helpful definition from our teacher team:
These are shapes that have three dimensions: length, width and depth. They differ from 2D shapes, which only have two dimensions (length and width).
The other key difference between two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects is that 3D objects have volume. Volume refers to the amount of space inside the 3D object.
What Are the Properties of 3D Shapes?
In addition to learning the correct mathematical names of the 3D shapes they are familiar with (more on that later!), students in elementary school are taught that these objects have specific properties. The properties of three-dimensional objects are their faces, edges and vertices. The number of faces, edges and vertices varies from one 3D shape to another.
Faces
A face on a three-dimensional shape is any flat surface on the outside of the object with straight edges. The square base on a square-based pyramid is an example of a face.
Edges
An edge refers to the straight line that is formed when two faces of a 3D shape meet. Using the previous example of the square-based pyramid, this 3D shape has four edges around the base. These edges occur where the square face at the bottom of the pyramid meets the triangular faces that make up the sides of the pyramid.
Vertices
A vertex on a 3D shape is any point where two edges meet. Another word commonly used as a synonym for vertice is ‘corner.’ Returning to our square-based pyramid, this 3D shape has four vertices at the base, and one at the very top where the edges of the four triangular faces meet.
What Are Some Examples of 3D Shapes?
Most kids are familiar with the overarching concept of a 3D shape. After all, these objects are to be found everywhere in our immediate environments! Think of household items such as books, soda cans, boxes of cereal, balls and so on. But do they know the mathematical names of these familiar objects? Some students may, but the vast majority probably don't!
That is why teachers must explicitly teach the mathematical names of these familiar objects.
Here are some of the more common 3D shapes your students will encounter during their primary school education:
Prism
Prisms are 3D objects that have the same 2D shape at each end. The sides that connect these end faces together are rectangular. Prisms are named after their cross-section. The cross-section of a prism is the shape that is made by cutting vertically down through the object. For example, a prism with a triangular cross-section is called a triangular prism.

Rectangular prisms are common 3D shapes found in the real world and in math class!
Sphere
A sphere is a ball-shaped 3D object. It is perfectly symmetrical. A sphere has one curved surface. It has no faces, edges or vertices.
Pyramids
Pyramids are 3D objects with triangular sides that meet together at the top (called the apex). The base of a pyramid can be any 2D shape, and this shape gives the pyramid its name.
For example, a pyramid with a hexagon as its base is called a hexagonal pyramid.

When a pyramid has a square base, this 3D shape is called a square pyramid, like the image above.
Cone
Don't be fooled... a cone may look a little like a pyramid, but it is a 3D object in its own right! A cone has a circular base and one curved surface that tapers to a single point (the apex). The apex sits directly above the centre of the base circle.
Cylinder
A cylinder is a 3D object similar to a soda can. It has two identical ends which are circular in shape. One curved surface joins the two circular ends together.
Do 3D Shapes Have Lines of Symmetry?
Good question! When exploring two-dimensional shapes, students are taught about lines of symmetry: imaginary lines that divide a shape into two equal halves that are an exact reflection of each other. When exploring 3D objects, it seems natural that the concept of symmetry may crop up!
Unlike their two-dimensional counterparts, three-dimensional objects do not have lines of symmetry. It is important for students to understand that because they have depth (as well as length and width), three-dimensional objects cannot be made symmetrical using a single line. It takes multiple lines that form a 2D shape to create what is called a "plane of symmetry" within a 3D object.
What Are 3D Shape Nets?
One highly effective way to teach your students about the properties of 3D shapes is to have them construct their own 3D models using nets. These nets are essentially a flattened-out version of a 3D shape that can be cut out, folded and adhered together to create a model of that particular 3D shape.
Best of all, 3D nets are great teaching tools to help students understand the properties of these shapes, as they can see and count the faces, edges and vertices with greater ease and accuracy.
- Plus Plan
Pot of Gold Sort - 2D and 3D Shapes
Sort coins that feature 2D shapes and 3D objects into their corresponding pots with a St. Patricks Day theme!
- Plus Plan
3D Astronaut Template
Create astronauts with this 3D net.
- Plus Plan
2D and 3D Shapes Vocabulary Poster
A poster that explains 2D and 3D shapes and lists associated vocabulary.
- Plus Plan

2D and 3D Shape Posters
Use this set of 14 brightly colored 2D and 3D shape posters to decorate your classroom and build academic vocabulary.
- Plus Plan

Halloween 3D Objects
Build some spooky Halloween characters with this set of five 3-D net templates.
- Plus Plan
3D Shape Profiles – Template
Draw, name, and describe the features of 3D figures with this profiling template.
- Plus Plan
Geometry Toss - Active Learning Game
Explore the differences between 2D shapes and 3D objects with an active game!
- Plus Plan
Memory Matcher PowerPoint – 3D Shapes
Recognize and recall the names of some of the most common 3D objects with a digital memory game!
- Plus Plan

Real Life 3D Shapes – Interactive PowerPoint
Explore three-dimensional objects in the real world with this engaging interactive activity.
- Plus Plan
2D and 3D Shape Flashcards
Explore 2D shapes and 3D objects with this set of 20 full-page flashcards.
- Plus Plan
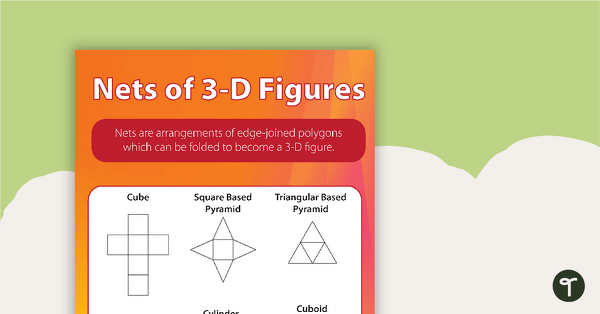
Nets of 3D Shapes - Poster
A poster highlighting the nets of a selection of 3D shapes.
- Plus Plan

2D and 3D Shapes - Cut and Paste Worksheet
Learn the difference between 2D shapes and 3D objects with this cut-and-paste worksheet.
- Plus Plan

Block Beasties – Task Cards
Create fabulous block beasties with this set of differentiated construction task cards.
- Plus Plan
3D Shapes Bingo
Learn the names of the most common 3D objects with this whole-class Bingo game.
- Plus Plan
3D Shapes Dominoes
A set of dominoes to help students reinforce their understanding of 3-D figures.
- Plus Plan
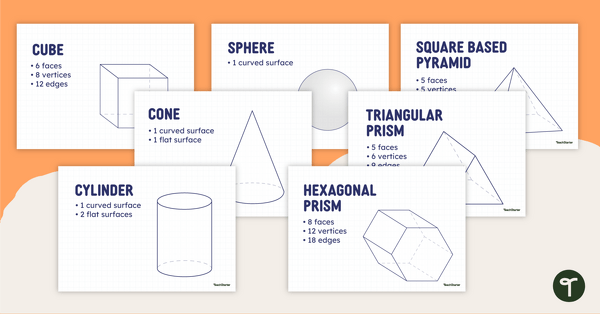
3D Shapes Anchor Chart Pack
Learn the names and properties of some common 3D shapes with this set of classroom anchor charts.
- Plus Plan

Let's Sort It! - 2D and 3D Shapes
Play this sorting game when learning about the properties of 2D and 3D shapes.
- Plus Plan

3D Shapes and Their Attributes - Puzzles
Explore the names and properties of some of the most common 3D shapes with this set of 8 puzzles.
-

10 Teacher-Tested Visual Brain Teasers to Try in Your Classroom
Using visual brainteasers in the classroom encourages critical thinking in your students - plus kids love them!
-
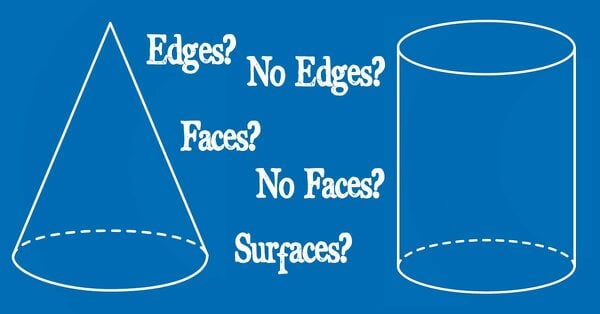
Solving the Cone and Cylinder Debate Once and for All
The debate is over...we have come to our final decision.